on
Demonstrating OAuth 2.0 using Facebook's Graph API
Introduction
OAuth 2.0 is regarded as the industry-standard protocol for authorization. It works by delegating user authentication to the service that hosts the user account (trusted identity provider), and authorizing third-party applications to access the user account.
This post focuses on implementing the OAuth flow to authorize a Facebook app to access user data.
OAuth Roles
- Resource Owner - A user who authorizes an application to access their data.
- Client - The application that wants to access protected resources.
- Resource Server - The service that holds user data
- Authorization Server - This service verifies the identity of a pending user.
The Resource Server and Authorization Server roles can be (and usually is) combined to form an API that fulfills both service roles.
Protocol Flow
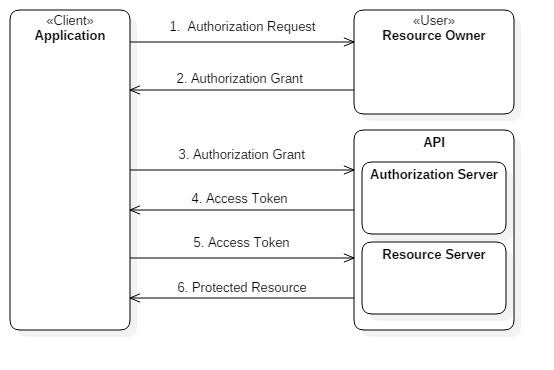 High level overview of OAuth protocol flow
High level overview of OAuth protocol flow
- The application requests authorization to access protected resources from the User.
- When the user authorizes the request, the application receives an authorization grant. (The grant types will be discussed briefly later on)
- The application requests for an Access Token from the authorization server (API) in exchange for the authorization grant. (Application identity details too are sent along with the authorization grant to the API token endpoint)
- The authorization server (API) issues an Access Token when both application identity and authorization grant are validated.
- The Application requests the protected resource from the API while presenting the Access Token for authentication.
- If the token is valid, the resource endpoint serves the resource to the application.
Application Registration
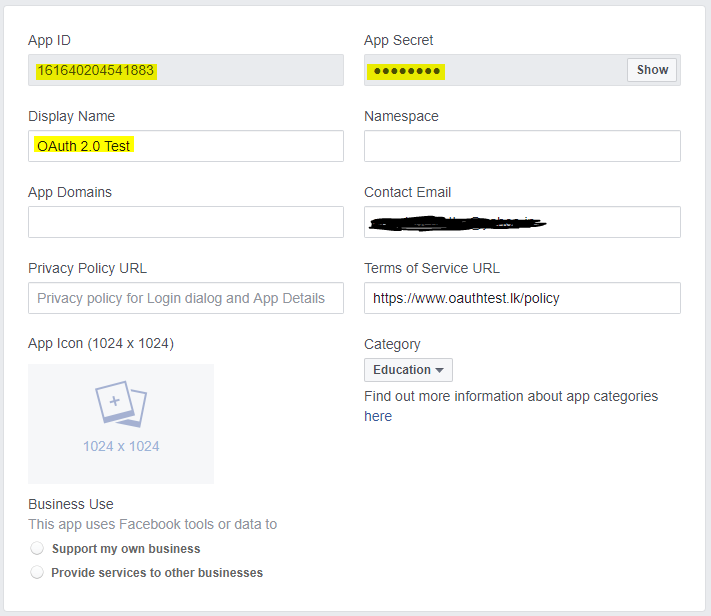 Application Registration fallout on Facebook Developers
Application Registration fallout on Facebook Developers
Before using OAuth with an application, the application must be first registered with the service.
Client ID and Client Secret
Once the application is registered, the service will issue "client credentials". It consists of a client identifier and a client secret. (A username-and-password-like combination) The Client ID is a publicly exposed string that is used by the service API to identify the application. The Client Secret is used to authenticate the identity of the application to the service API when the application requests to access a user's account. It must be kept private between the application and the API. Implementing client side code with the Client Secret in plain is a huge security risk.
Callback URLs
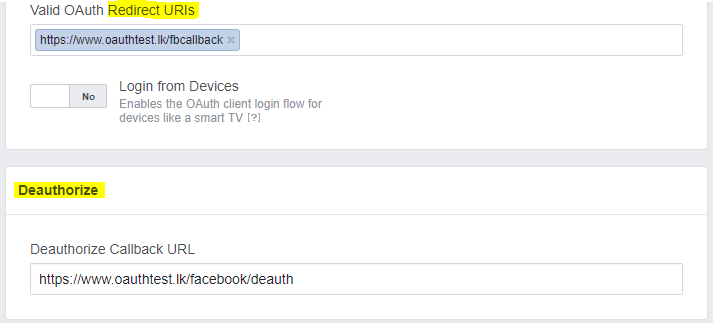 Callback URLs for the application
Callback URLs for the application
Redirect URLs must be pre-configured into the service before exposing them via the client code. These will determine where a user is redirected upon the authorization result.
Authorization Grant
OAuth 2.0 defines four grant types, each of which is useful in different cases:
- Authorization Code: used with server-side Applications
- Implicit: used with Mobile Apps or Web Applications (applications that run on the user's device)
- Resource Owner Password Credentials: used with trusted Applications, such as those owned by the service itself
- Client Credentials: used with Applications API access
Authorization Code Grant Type
The authorization code grant type is the most commonly used because it is optimized for server-side applications. Because the server-side source code is not publicly exposed, Client Secret confidentiality can be maintained.
Authorization Code Link
The user is prompted to click on a button or link that resembles the following format.
https://www.facebook.com/v2.12/dialog/oauth?client_id=161640204541883&state=2081c5c62987cf1a760e3833295f3ea2&response_type=code&sdk=php-sdk-5.6.2&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.oauthtest.lk%2Ffbcallback&scope=email%2Cpublic_profile%2Cuser_posts%2Cuser_friends%2Cpublish_actions
The link components are as follows.
- https://www.facebook.com/v2.12/dialog/oauth: the authorization endpoint of Facebook's graph API v2.12.
- client_id: the application's client ID
- state: a random string that serves CSRF protection
- response_type: code - specifies that the application is requesting an authorization code grant
- redirect_uri: where the service redirects the user-agent after an authorization code is granted
- scope: specifies the level of access and/or permissions to resource groups.
- sdk: php sdk version. This is optional
public function show()
{
$fb = new Facebook(
'app_id' => env('FB_APP_ID'),
'app_secret' => env('FB_APP_SECRET'),
'default_graph_version' => env('API_VERSION'),
]);
$helper = $fb->getRedirectLoginHelper();
$permissions = ['email', 'public_profile', 'user_posts', 'user_friends', 'publish_actions',];
$loginUrl = $helper->getLoginUrl('https://www.oauthtest.lk/fbcallback', $permissions);
$url = htmlspecialchars($loginUrl);
return view('index')->with('url', $url);
}
User Authorizes the application
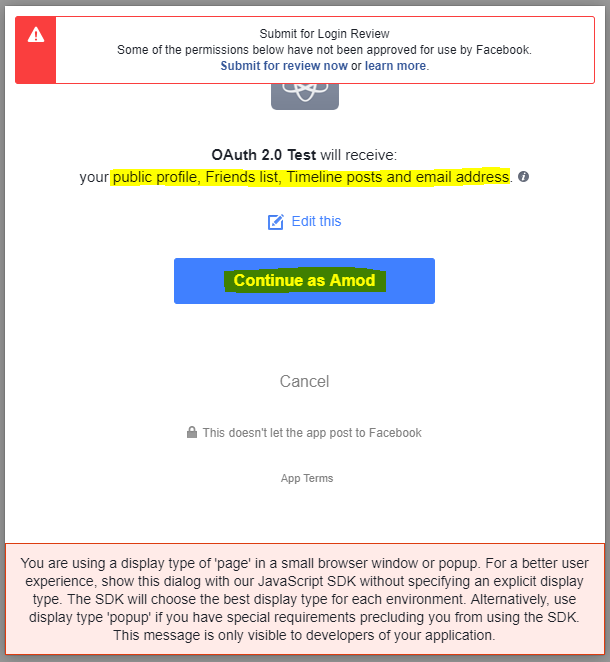
When the user clicks the link, the user-agent (browser) is redirected to the identity service (i.e. Facebook) to authenticate the user's identity. The user must login to the service if they're not logged in already.
Application Receives Authorization Code
When the user authorizes the application, the service redirects the user-agent to the application redirect URL, which was specified during the client registration, along with an authorization code and the state parameter. The redirect would look something like this.
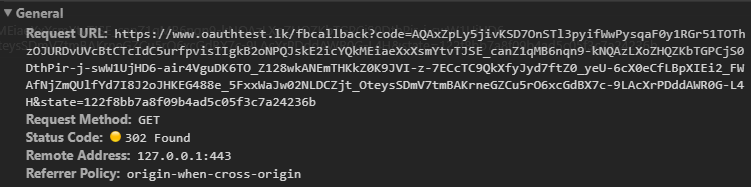
Application Requests Access Token
The application requests an access token from the API, by passing the authorization code along with authentication details, including the client secret, to the API token endpoint.
GET https://graph.facebook.com/v2.12/oauth/access_token? client_id={app-id} &redirect_uri={redirect-uri} &client_secret={app-secret} &code={code-parameter}
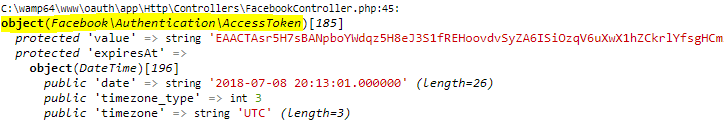
Application Receives Access Token
If the authorization is valid, the API will send a response containing the access token to the application.
$helper = $fb->getRedirectLoginHelper();
$_SESSION['FBRLH_state'] = $_GET['state'];
try {
$accessToken = $helper->getAccessToken(); //the SDK does a post to the token endpoint
} catch (FacebookSDKException $e) {
echo 'Facebook SDK returned an error: ' . $e->getMessage();
exit;
}